Revolutionizing Taste TechnologyWorld’s First Artificial Tongue That Can ‘Taste and Learn’ Like a Human Organ.”Revolutionizing Taste Technology
Revolutionizing Taste Technology
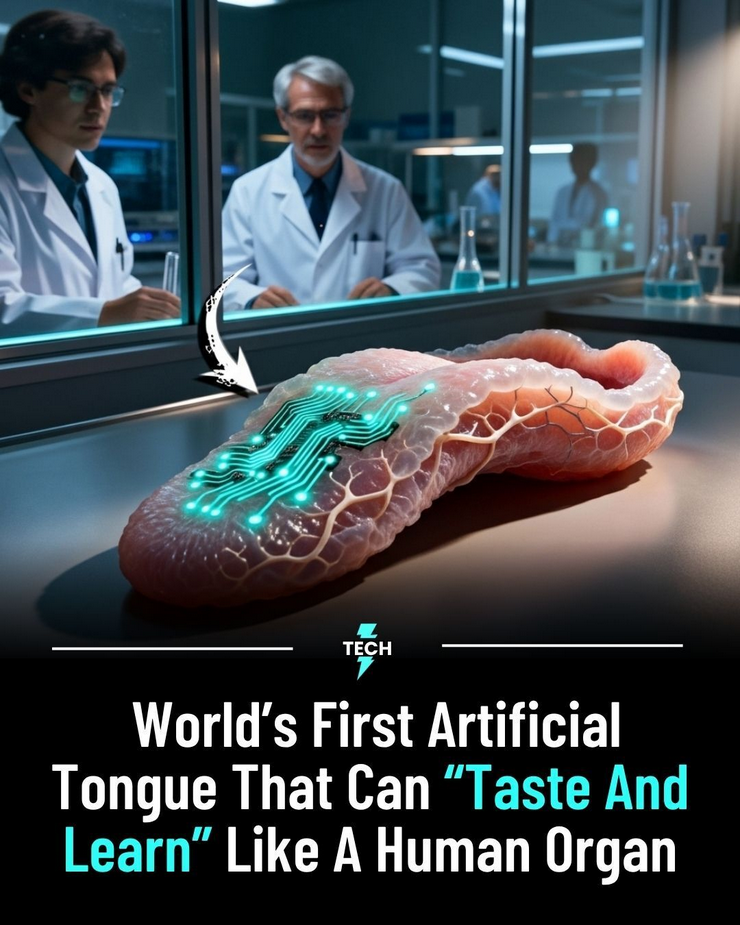
Scientists have developed the world’s first artificial tongue capable of not only detecting flavors but also learning and adapting like a real human organ. This breakthrough in bio-inspired technology combines sensors, machine learning, and biochemical analysis to replicate the complex taste perception process, opening doors for applications in food testing, healthcare, and robotics.
The artificial tongue can identify sweet, sour, salty, bitter, and umami flavors, as well as more subtle taste profiles, by analyzing chemical compounds in food and beverages. Its learning algorithms allow it to improve accuracy over time, mimicking how humans refine their sense of taste through experience. Researchers believe this innovation could revolutionize quality control in the food industry, assist in developing healthier products, and even aid patients with taste disorders.
Experts also see potential applications in robotics, where artificial taste sensors could enhance decision-making for autonomous systems in food production, agriculture, and environmental monitoring. By combining artificial intelligence with bio-inspired engineering, the technology represents a major step toward creating machines that can perceive and interact with the world more like humans.
This artificial tongue marks a milestone in sensory technology, merging biology and AI to create tools that can learn, adapt, and transform how we understand taste.
